
[ad_1]
If you cannot delete a file or folder on an NTFS file system volume, this post will help you resolve the issue. There are various cases, and we will talk about all of them in detail in this article. So, if you can’t delete a file or a folder on an NTFS file system volume, follow the solutions mentioned in this post.

Fix Can’t delete a file or a folder on an NTFS file system volume
If you can’t delete a file or a folder on an NTFS file system volume on your Windows computer, you fall under one of the following cases.
- An Access Control List (ACL) is being used
- You can’t delete the file as it is being used
- The file system is corrupted
- The file name includes a reserved or invalid name in the Win32 name space
- Files path exceeds MAX_PATH
Let us talk about them in detail.
1] An Access Control List (ACL) is being used
If you’re trying to delete a file that uses an Access Control List (ACL), you may encounter an issue as the file cannot be deleted. To fix this problem, you’ll need to change the permissions on the file. In some cases, you may also need to take ownership of the file to change its permissions.
As an administrator, you have the implicit ability to take ownership of any file, even if you haven’t been explicitly granted any permission to the file. File owners also have the implicit ability to modify file permissions, even if they haven’t been explicitly granted any permissions to the file. Therefore, you might need to take ownership of a file, give yourself the necessary permissions to delete the file, and then delete it.
One still might get the following prompt.
You can’t use certain security tools to display or to modify permissions because the file has a non-canonical ACL
If you get this prompt, you need tools such as Cacls.exe.
ACEs in an ACL have a preferred sequence based on their type. In earlier Windows versions, non-canonical ACLs caused issues. Use the latest version of Cacls.exe if you experience this problem. You can write a new ACL to gain file access if you can’t modify it in place.
Related: The Access Control List (ACL) structure is invalid
2] You can’t delete the file as it is being used
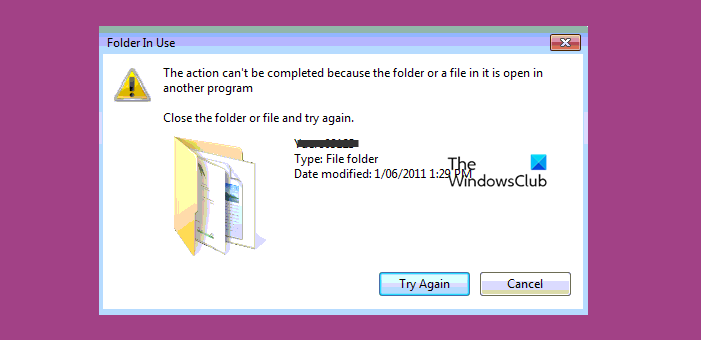
If you can’t delete the file as it is being used, make sure to kill all the related processes and associated applications. If a file is being used in a shared environment, you may not be able to delete it now. When all the users withdraw from the application, then only you will be able to delete that particular file. However, there are certain applications, including Task Manager, to find out what’s open.
3] The file system has been corrupted
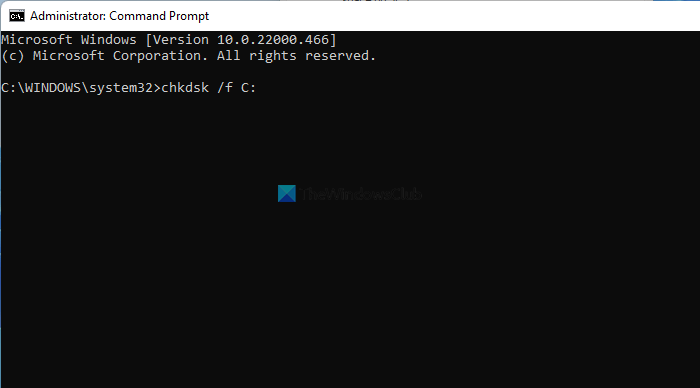
If the file system itself is corrupted, you won’t be able to delete its files. You can use the Check Disk command to find out bad sectors and repair them:
chkdsk /r
However, you may also experience this issue if your hard drive is faulty. In that case, consult a hardware expert and ask them to make the needed changes.
4] The file name includes a reserved or invalid name in the Win32 name space
To delete a file with a reserved name like “lpt1”, use a non-Win32 program to rename it. Or, use specific syntax with built-in commands to bypass Win32 checks. Certain file names are reserved for old-style DOS devices and can’t be created with typical Win32 calls. Use the same technique to traverse deeper folders or POSIX tools to bypass name checks.
If the file has a trailing space or a trailing period in its name or any other term that makes it incompatible with the Win32 naming convention, you won’t be able to delete the file. So, we would recommend you use a tool that uses the correct internal syntax. You can go with “\\?\” as it works with certain tools nonchalantly.
Read: Windows must be installed to a partition formatted as NTFS
5] Files path exceeds MAX_PATH
You can’t open, edit, or delete a file if its path exceeds MAX_PATH. In this case, follow the solutions mentioned below.
- Use the autogenerated 8.3 name to access the file: If long folder names are causing issues while accessing a deep path, try this resolution.
- Rename the folder: Rename the folder so that the target files that are deeper than the no longer exist. If you do so, start at the root folder or any other convenient place. Then, rename folders so that they have shorter names.
- Map a drive to a folder inside the structure of the path of the target file or folder: Here, we aim to shorten the virtual path. We need to make sure that the length of this path is 73 characters by mapping a drive to SubfolderName4.
- Create a network share that’s as deep as the folder: You should create a network share that’s as deep in the folder tree as possible and rename the folders by accessing the share.
- Traverse deep paths: Windows programs have a maximum path length of 255 characters, which is shorter than the limit of NTFS. This means that some programs may not be able to handle longer paths. If you create a share at some point in your folder structure that’s already fairly deep, and then create a deep structure below that point by using the share, you may experience this issue. Some tools that operate locally on the folder tree may not be able to traverse the whole tree starting from the root. You may have to use these tools specially so that they can traverse the share.
Hopefully, you can resolve the issue using the solutions mentioned in this post.
Read: How to convert Hard Disk or Partition to NTFS format in Windows
What happens when you delete a file from an NTFS file system?
When a file is deleted, its name in the directory changes its first letter to a sigma. After this, the storage location of the file is marked as unallocated, which means it may be overwritten. However, it is still possible to search for and recover the deleted file using certain techniques.
Read: How to enable or disable NTFS File Compression in Windows
How do I delete a folder that won’t delete?
If you can’t delete the folder normally, you should boot into Safe Mode and then delete it. In Safe Mode, startup programs and add-ons do not run. Safe Mode is usually used for troubleshooting issues.
Read: NTFS FILE SYSTEM Blue Screen error on Windows.

[ad_2]
Source link
www.thewindowsclub.com